Environment
(E)
Environmental preservation through compliance with regulations and verification of environmental policies and performance
Social
(S)
Responsible management through improvement of working conditions and respect for human rights
Governance
(G)
Board activities and legal compliance, supported by audit systems for ethical and transparent management
CSR
UVER strengthens information security to protect both corporate confidentiality and customer data. We are committed to responsible supply chain management by adhering to international standards that regulate the use of conflict minerals.
Information Security Commitment
All employees recognize the importance of protecting the company’s valuable information assets and continuously engage in improvement activities.
Employees shall comply with all relevant laws and regulations on information security and fulfill their roles and responsibilities in protecting information.
Employees shall establish and execute training plans on information security and continuously strive to enhance these efforts.
Personal data related to employees shall be managed through regular monitoring and audits in accordance with the Personal Information Protection Act.
Confidential information, including trade secrets and strategic business plans, must not be disclosed or removed without prior company authorization.
Proactive Information Security Measures
- Conducting information security training for new hires and departing employees
- Managing usage logs of computers and storage devices
- Regularly updating and managing passwords for company email accounts
Quality Management
To ensure customer satisfaction, UVER is committed to providing high-quality products and services. We achieve quality competitiveness through strict adherence to standard operating procedures and continuous optimization of production processes.
Establishing and Maintaining Core Quality Standards
- Executing standardized work procedures based on official manuals and instructions
- Stabilizing the work environment through enhanced 3S and 5S practices
Strengthening Quality Control (QC) on the Line
Assigning and managing dedicated quality personnel for each process
Reinforcing quality checks at every stage of production
Enhancing Workplace Management
Enforcing work attire standards specific to each process
Strengthening particle control in cleanroom environments
Maintaining cleanliness, organization, and discipline in all work areas
Operation of Quality CS Team
Domestic/International support
24-hour emergency response
Conflict Minerals
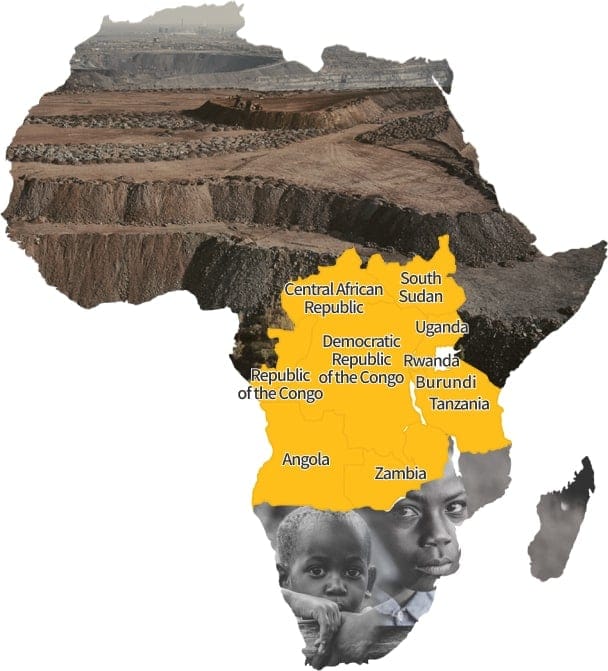
Conflict minerals refer to four primary minerals—tin, tantalum, tungsten, and gold (collectively known as 3TG)—mined in regions of armed conflict in Africa, including the Democratic Republic of Congo, Sudan, Rwanda, Burundi, Uganda, Zambia, Angola, Tanzania, the Central African Republic, and other countries. In these areas, armed groups, including rebel and government forces, control the extraction and distribution of these minerals. This control has led to significant social issues, including human rights violations and the exploitation of local labor. To address these issues, regulations have been enacted to restrict the use of conflict minerals by companies as part of broader economic sanctions aimed at combating human rights abuses in these regions.
These minerals are used across a wide range of industries, including mobile phones, electronics, and automotive components.
In July 2010, the U.S. Congress passed the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, followed by U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulations on August 22, 2012. As a result, U.S.-listed companies, including emerging growth companies, are required to investigate the use and origin of conflict minerals by May 31 each year, conduct due diligence on their supply chains, and report their findings to the SEC.
10 African conflict-affected countries and conflict minerals
Reserves and Uses of Conflict Minerals
| Mineral | Reserves | Key Applications | Core Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tin | 3~4% | Electronic soldering, industrial equipment, chemical compounds, etc. | Mobile phones, automotive, jewelry, electronic, medical devices, etc. |
| Tantalum | 8~20% | Electronic capacitors, turbine components, chemical processing equipment, etc. | Mobile phones, automotive, aerospace, energy, etc. |
| Tungsten | 2~4% | emented carbide tools, electron guns, etc. | Automotive, electronic medical devices, energy, etc. |
| Gold | 1% | Electroplating, Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) | Semiconductors, aerospace, etc. |
Conflict Minerals Policy
- UVER is committed to ensuring legal compliance by adhering to international standards regulating conflict minerals, in partnership with our suppliers. We will actively participate in initiatives to prohibit the use of conflict minerals, as promoted by the EICC (Electronic Industry Citizenship Coalition) and GeSI (Global e-Sustainability Initiative), in order to fulfill our social responsibility in protecting human rights in conflict-affected regions of Africa.
- We will use the Conflict Minerals Reporting Template provided by EICC-GeSI to identify the names and locations of all smelters involved in the refining of tin, tantalum, tungsten, and gold used in our products.
- We will require our suppliers to submit the Conflict Minerals Reporting Template and confirm that they do not use conflict minerals.
- In accordance with our internal standards, we will ensure that all suppliers are fully aware of relevant conflict mineral regulations and strictly comply with our conflict minerals policy.

